Survey Two 2002
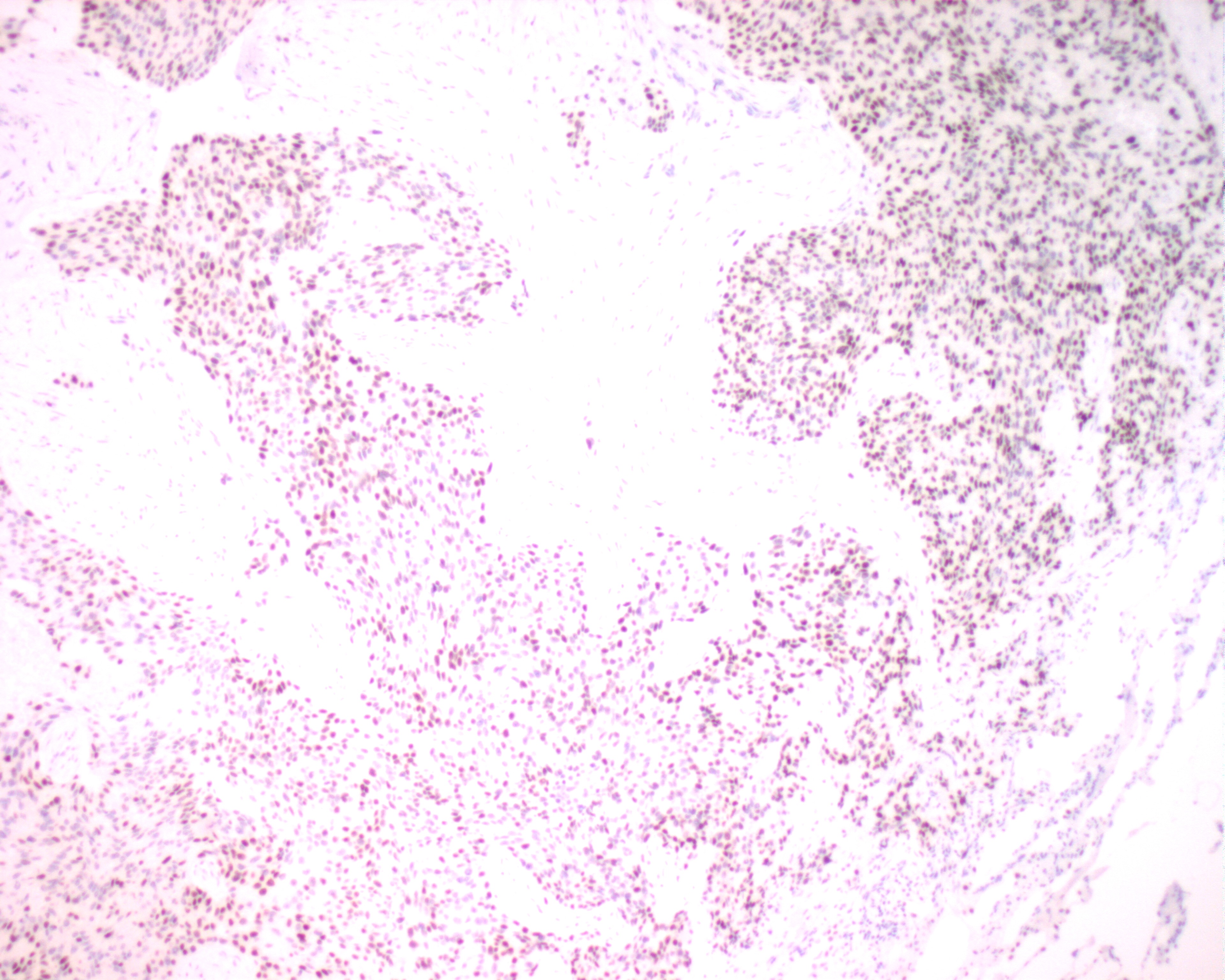
Supplied TTF-1
| A section of a poorly
differentiated lung carcinoma shows desmoplastic fibrous tissue infiltrated by sheets of cohesive
malignant tumour cells, which possess hyperchromatic enlarged nuclei with occasional prominent
nucleoli. Positive nuclear staining of thyroid transcription factor-1 (TTF-1) helps in the
classification of tumours of the lung and thyroid. The antibody was found to react positively with
the primary and metastatic pulmonary adenocarcinomas, and the majority of pulmonary small cell
carcinomas and large cell carcinomas, whereas reacting negatively with squamous cell carcinomas of
the lung. TTF-1 has also been detected in thyroid papillary carcinomas. The antibody is
immunoreactive with Type II cells and Clara cells of the lung and follicular cells from thyroid,
but not other normal tissues. |
 |
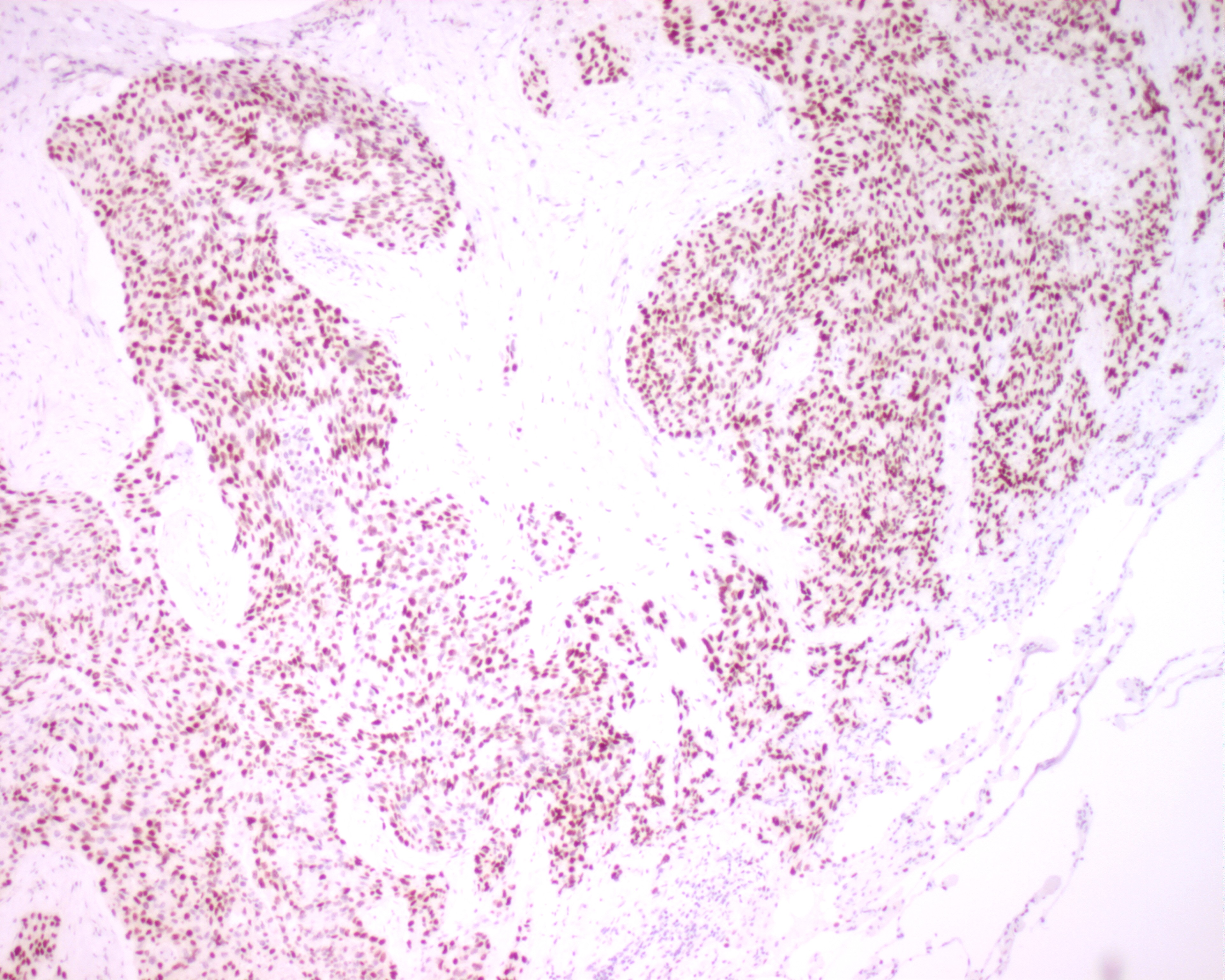
In-house TTF-1
| A section from same tissue
block is immunostained with in-house TTF-1. The average result is comparable with that stained with
supplied antibody. The best results for both supplied and in-house TTF-1 are
obtained by peroxidase
blocking for 10 min., pressure cooking treatment for 2.5 min., and immuno-stained with 1:40, supplied,
versus 1:50, in-house, diluted primary antibody for 32 min. at 37 oC. |
 |
References:
Holzinger A, et al. Monoclonal antibody to thyroid transcription factor-1: Production,
characterization and usefulness in tumor diagnosis. Hybridoma 1996; 15(1):49.
Anderson SS, et al. Thyroid transcription factor-1 (TTF-1) is a more sensitive lung carcinoma marker
than surfactant ApoA1. Lab Invest 1998; 78(1):171A(1001).
Srodon, Westra. Immunohistochemical staining for thyroid transcription factor-1: A helpful aid in
discerning primary site of tumor origin in patients with brain metastases. Hum Pathol 2002; 33:642-45.

Last updated on 3 November, 2002.
Prepared by HKIMLSQAP Anatomical Pathology Panel.
Copyright 2001-2002 HKIMLSQAP. All Rights Reserved.
